Exploring the Benefits and Applications of Illuminated Rotary Encoders
Sep 12,2025
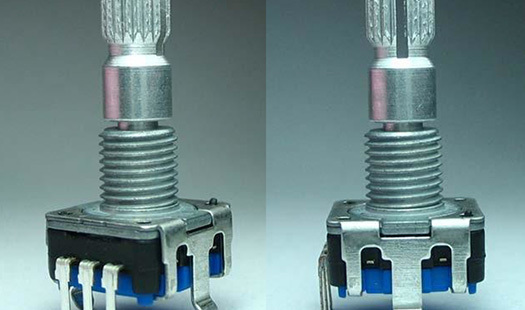
Illuminated rotary encoders are essential components in modern electronic systems, serving as a bridge between user input and electronic control. These devices combine the functionality of traditional rotary encoders with the added advantage of built-in illumination, enhancing user experience and visibility. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of illuminated rotary encoders, focu
Illuminated rotary encoders are essential components in modern electronic systems, serving as a bridge between user input and electronic control. These devices combine the functionality of traditional rotary encoders with the added advantage of built-in illumination, enhancing user experience and visibility. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of illuminated rotary encoders, focusing on their operational principles, benefits, and applications across various industries.
At their core, rotary encoders are sensors that translate rotational motion into electrical signals, which can be interpreted by electronic systems. They are primarily used to measure the position, speed, and direction of rotation. When equipped with illumination, these encoders offer an added layer of practicality. The illumination, often LED-based, enhances visibility in low-light environments, making them ideal for applications where user interaction is critical, such as in control panels, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics.
One of the key advantages of illuminated rotary encoders is their ability to improve user interface design. In critical environments, such as medical equipment or aerospace control systems, the visibility provided by the illumination helps operators make precise adjustments, reducing the likelihood of errors. This feature is particularly valuable in applications where operators might need to interact with the device in dimly lit conditions, ensuring that the rotary encoder can be easily located and utilized.
Moreover, illuminated rotary encoders can also provide visual feedback to users. For instance, different colors or flashing patterns can indicate specific status conditions or modes of operation. This immediate visual feedback can enhance user understanding and engagement, making the overall experience more intuitive. Such feedback mechanisms are critical in applications ranging from gaming controllers to high-tech industrial controls, where real-time information is vital.
The versatility of illuminated rotary encoders extends across various industries. In consumer electronics, they are commonly found in audio equipment, allowing users to adjust volume levels with ease while providing visual cues for status changes. In automotive applications, these encoders might be used in dashboard controls, where illumination not only aids visibility but also adds an aesthetic component to the vehicle's interior design.
In conclusion, illuminated rotary encoders represent a significant advancement in sensor technology, combining functional performance with enhanced usability and visual appeal. As industries continue to seek ways to improve user interactions and operational efficiency, the demand for such innovative devices is likely to grow, paving the way for more intuitive and user-friendly electronic systems. Whether in industrial settings, consumer electronics, or other fields, the application of illuminated rotary encoders is diverse and continues to evolve, offering exciting possibilities for the future of electronic interfaces.
At their core, rotary encoders are sensors that translate rotational motion into electrical signals, which can be interpreted by electronic systems. They are primarily used to measure the position, speed, and direction of rotation. When equipped with illumination, these encoders offer an added layer of practicality. The illumination, often LED-based, enhances visibility in low-light environments, making them ideal for applications where user interaction is critical, such as in control panels, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics.
One of the key advantages of illuminated rotary encoders is their ability to improve user interface design. In critical environments, such as medical equipment or aerospace control systems, the visibility provided by the illumination helps operators make precise adjustments, reducing the likelihood of errors. This feature is particularly valuable in applications where operators might need to interact with the device in dimly lit conditions, ensuring that the rotary encoder can be easily located and utilized.
Moreover, illuminated rotary encoders can also provide visual feedback to users. For instance, different colors or flashing patterns can indicate specific status conditions or modes of operation. This immediate visual feedback can enhance user understanding and engagement, making the overall experience more intuitive. Such feedback mechanisms are critical in applications ranging from gaming controllers to high-tech industrial controls, where real-time information is vital.
The versatility of illuminated rotary encoders extends across various industries. In consumer electronics, they are commonly found in audio equipment, allowing users to adjust volume levels with ease while providing visual cues for status changes. In automotive applications, these encoders might be used in dashboard controls, where illumination not only aids visibility but also adds an aesthetic component to the vehicle's interior design.
In conclusion, illuminated rotary encoders represent a significant advancement in sensor technology, combining functional performance with enhanced usability and visual appeal. As industries continue to seek ways to improve user interactions and operational efficiency, the demand for such innovative devices is likely to grow, paving the way for more intuitive and user-friendly electronic systems. Whether in industrial settings, consumer electronics, or other fields, the application of illuminated rotary encoders is diverse and continues to evolve, offering exciting possibilities for the future of electronic interfaces.
More Information
More Information
RECOMMENDED